# EMSC 3002 ## Fold Geometry - Louis Moresi (convenor) - **Romain Beucher** (lecturer) - Chengxin Jiang (lecturer) - Stephen Cox (curriculum advisor) Australian National University _**NB:** the course materials provided by the authors are open source under a creative commons licence. We acknowledge the contribution of the community in providing other materials and we endeavour to provide the correct attribution and citation. Please contact louis.moresi@anu.edu.au for updates and corrections._ <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/The_folds_of_the_rocks_at_position_Apoplystra.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Resources 1. **Fossen, H, 2011.** *Structural Geology.* Cambridge University Press, 2nd Edition **Chapter 11** 1. **McClay, K.R. 1991.** *The Mapping of Geological Structures.* John Wiley & Sons. **Chapter 3** 1. **Park, R.G., 1995.** *Foundations of Structural Geology.* Blackie & Sons Ltd. **Chapter 2** 1. **Davis, G.H. and Reynolds, S.J., 1996.** *Structural Geology of Rocks and Regions.* 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons. **Chapter 7** <!-- 1. **Hatcher, R.D., 1990.** *Structural Geology - Principles, Concepts, and Problems*, 2nd Edition, Prentice-Hall --> <!-- 1. **Ramsay, J.G. and Huber, M.I. 1983.** *Modern Structural Geology. Volume 1: Strain Analysis.* Academic Press. --> <!-- 1. **Ramsay, J.G. and Huber, M.I. 1987.** *Modern Structural Geology. Volume 2: Folds and Fractures.* Academic Press. --> <--o--> ## Intended learning outcomes Students will be able to: - Describe and name basic elements of fold geometry - Use classifications to describe fold styles <--o--> ## Folds, Why are they important? <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left"> Hydrocarbon industry: - Folds and associated structures can form traps. - Understanding folds periodicity and geometry is key for the selection of drilling sites. Mineral Industry: - Understanding folds structures is important in assessing the extent of ore reserves and the viability of mines. </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right"> 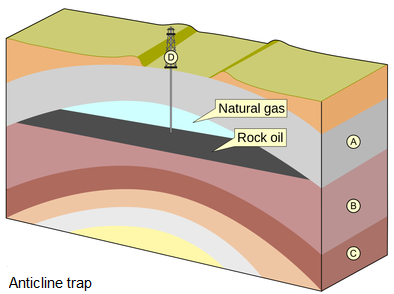 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="90%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Basic Elements of Fold Morphology The conditions of deformation usually vary both in space and time, differences in rock type, temperature, pressure and strain-rate translates in a wide range of fold geometry or **fold styles**. Correct interpretation of the variations in fold style is important to reconstruct the geological history of an area. <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Folds_near_Commana_in_Brittany_France_2.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Basic Elements of Fold Morphology ### Observation of folds in section  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="60%" --> **Folds** are usually best studied in section perpendicular to the layering, or perpendicular to what is defined as the **axial surface**. Folds are made up of a **hinge** that connects to **limbs**. The **hinge** may be abrupt but usually the curvature is gradual and define a **hinge zone**. <--o--> ## Basic Elements of Fold Morphology Accurate description of folded structures requires using a specific vocabulary. Key to compare natural structures across different contexts. 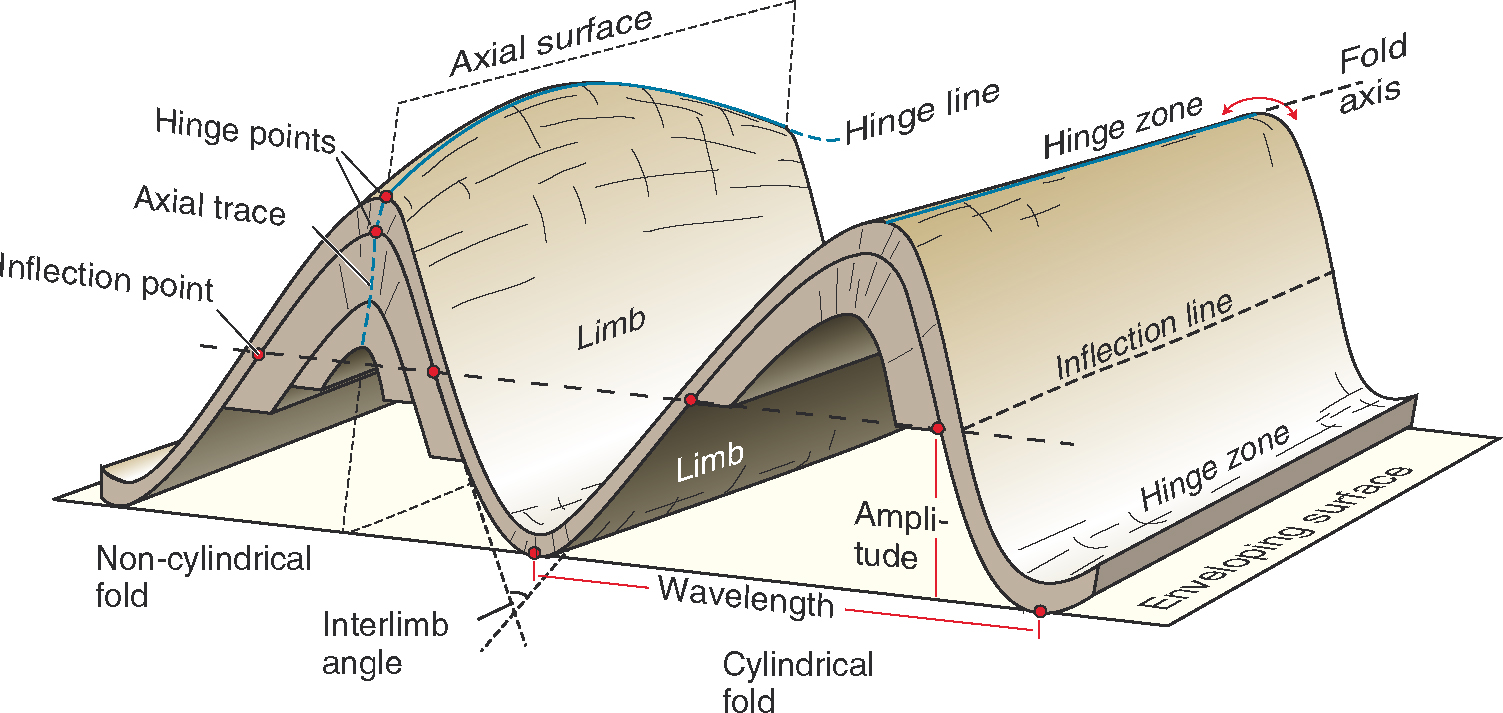 <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Tightness and Angularity (Interlimb angle) <div> <div style="width:70%; float:left">  <!-- .element width="95%" --> </div> <div style="width:30%; float:right"> <div>  <!-- .element width="90%" --> </div> <div> 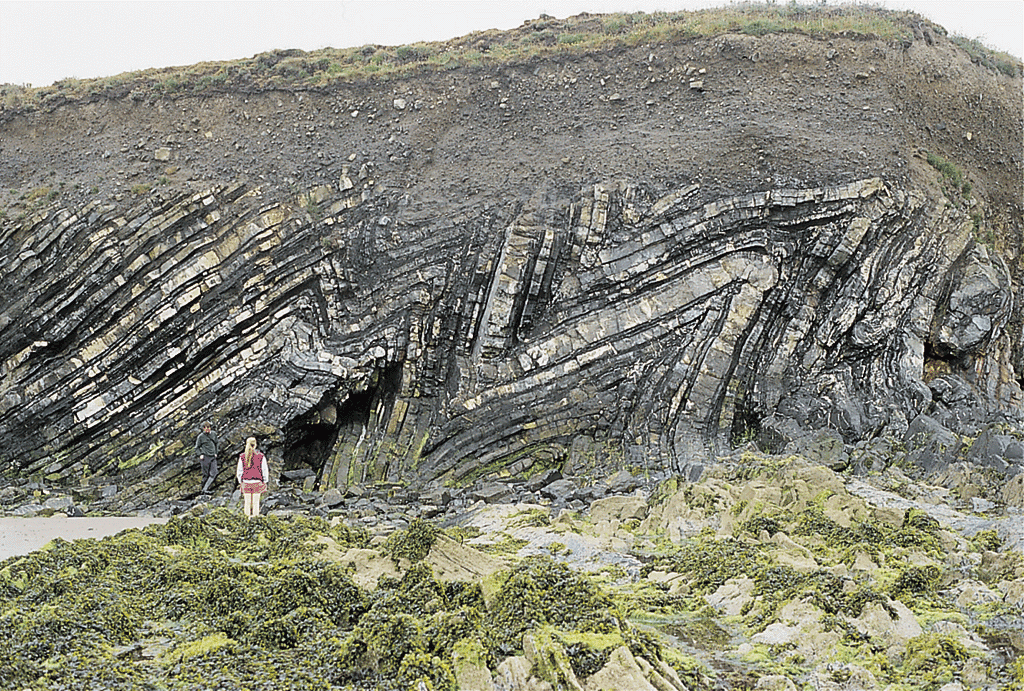 <!-- .element width="90%" --> </div> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Wavelength and Amplitude <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left"> The Shape of folds can be compared to mathematical functions. We use terms such as **amplitude** and **wavelength**. Folds do not necessarily follow the regularity of simple mathematical function. Nevertheless, simple harmonic analysis can be applied to describe fold shape. </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Cylindrical, non-cylindrical <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left"> Folds may be cylindrical so that the fold axis or hinges plunges in one direction. Especially on the large scale the fold may also be non-cylindrical with a fold axis that plunges in either direction. </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Basic Fold shapes <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  <!-- .element style="float: right" height="95%" --> </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" height="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Anticline 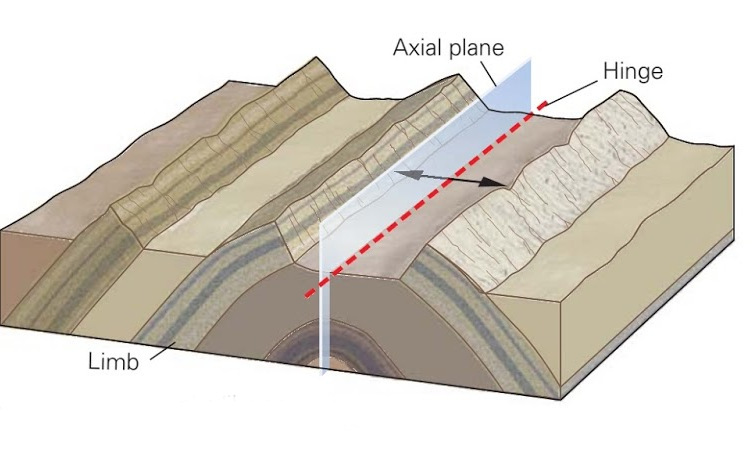 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Anticline.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Syncline 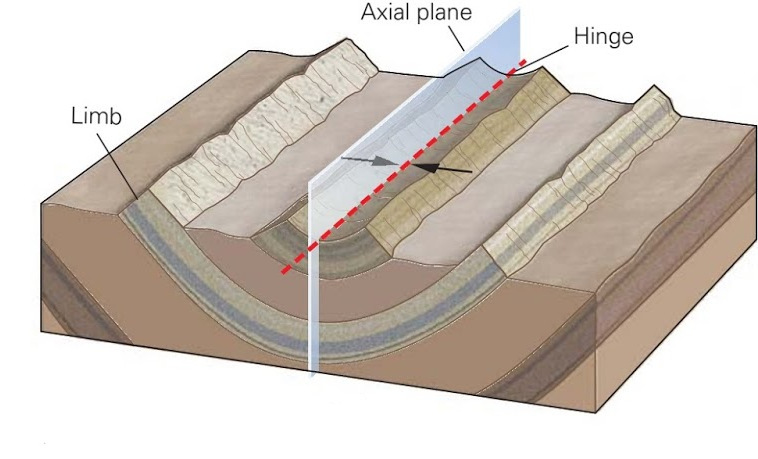 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/syncline-oklaoma_university.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Dome 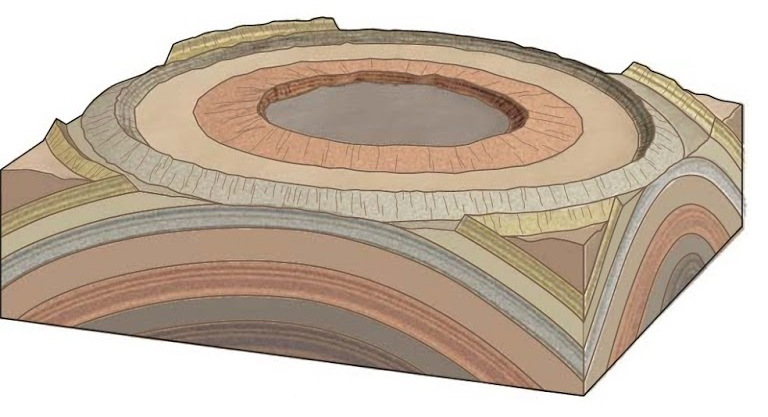 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Richat structure.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Basin 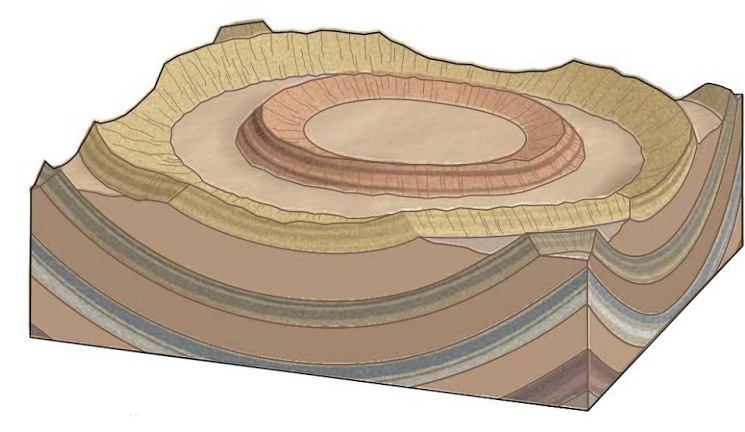 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> ## Fold shape and stratigraphy  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> ## Classification of folds  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> <--o--> ## Fold Styles <div> <div style="width:45%; float:left"> A spectrum of hinge shapes exists, from the pointed hinges of kink-bands and chevron folds to the rounded hinges of concentric folds. Classification according to the hinge curvature is referred to as bluntness. </div> <div style="width:55%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" height="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Kink Folds <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  <!-- .element style="float: left" width="95%" --> </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: left" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Concentric Folds <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> *Core of concentric anticline. Keele River, McKenzie Mountains, Northwest Territories, Canada. [64.170859,-125.598908]* </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Chevrons Folds <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> *Chevron folds with flat-lying axial planes, Millook Haven, North Cornwall, UK* source:  <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Box Folds <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold styles ### Ptygmatic Folds <div> <div style="width:50%; float:left">  </div> <div style="width:50%; float:right"> 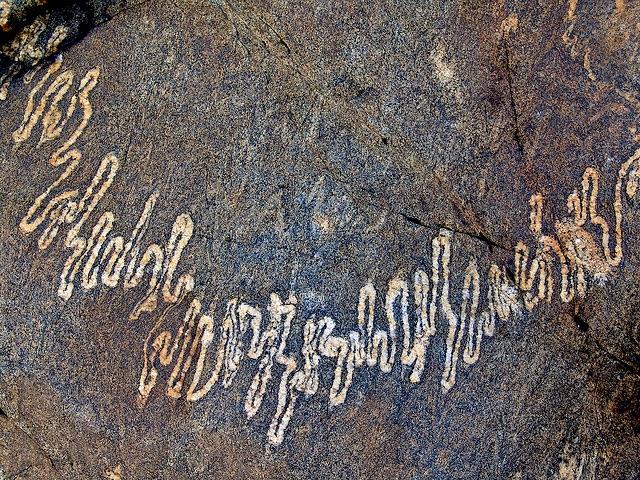 <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Geometric Aspects of folds <div> <div style="width:60%; float:left"> <!-- .element style="float: left" width="90%" --> </div> <div style="width:40%; float:right"> <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold Attitude  <!-- .element style="float: center" height="95%" --> <--o--> ## Fold Attitude <div> <div style="width:40%; float:left"> - Horizontal folds have horizontal fold axis. - Vertical folds have vertical fold axis. - Plunging folds have plunging fold axis. - Reclined folds have a plunging fold axis AND younging pointing downward. </div> <div style="width:60%; float:right">  <!-- .element style="float: right" width="95%" --> </div> </div> <--o--> ## Fold Attitude  <!-- .element style="float: center" height="95%" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Recumbent_Folds_Anne_Burges_CC.jpg" --> <--o--> ## Fold Attitude 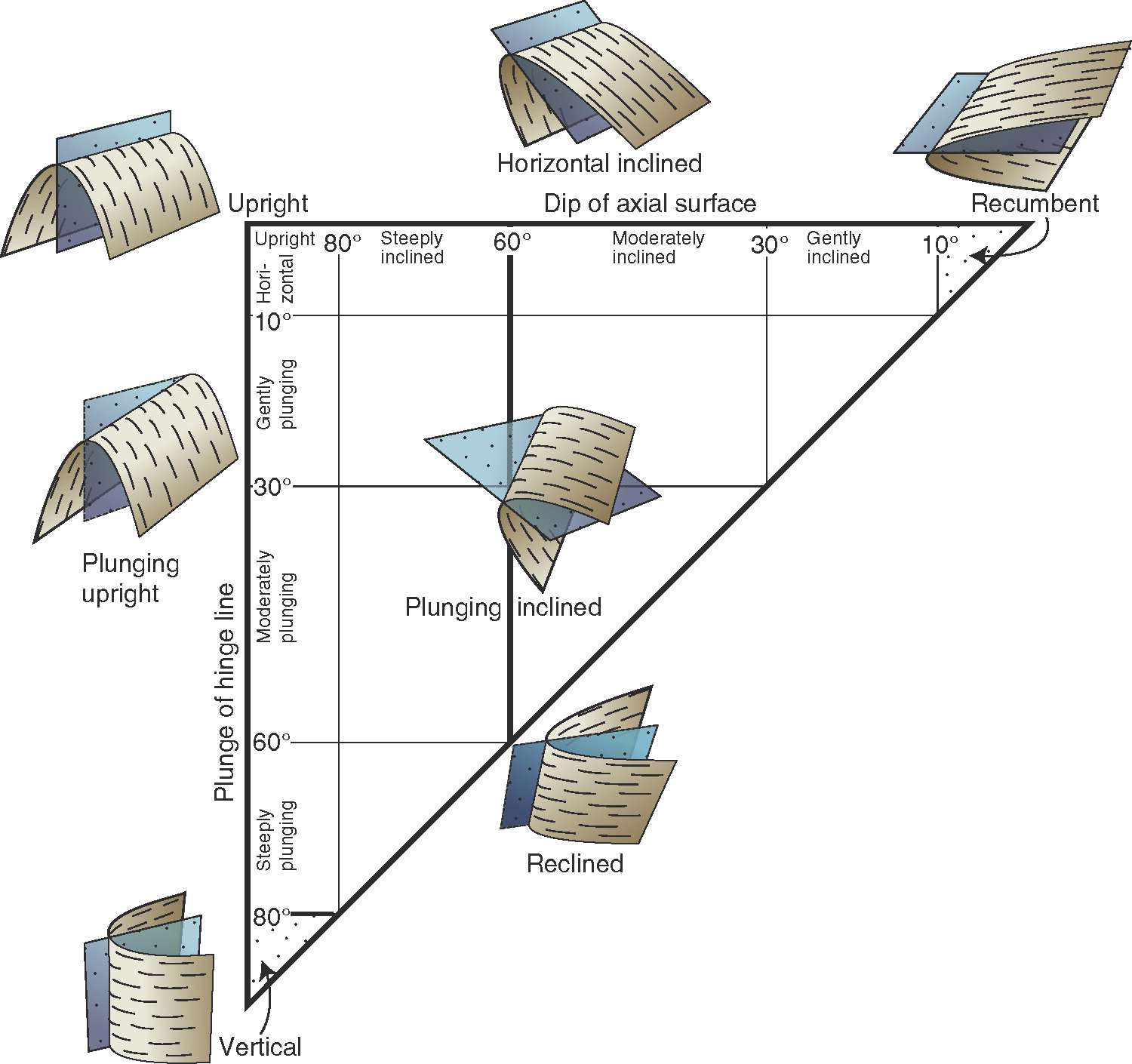 <!-- .element style="float: center" width="50%" --> <--o-->  <!-- .element style="float: center" width="100%" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Exceptional_folds_during_the_Girls_into_Geoscience_inaugural_Irish_Fieldtrip.jpg" --> <--o--> <!-- .slide: data-background="Module-v-Ductile-Deformation/Figures-Fold-Geometry/photos/Ptygmatic_folds_EGU_Blog_Iran.jpg" -->